Table of Contents
These days, 12 volt, 24V, and 48V energy storage systems tend to consist of batteries with the LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) chemistry.
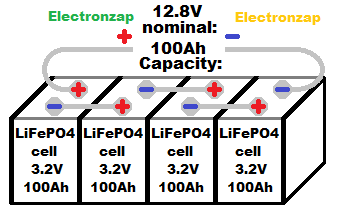
LiFePO4 cells have a nominal (average) voltage of 3.2V. Four cells are usually connected in series to make a battery with a nominal voltage of 12.8V. Manufacturers typically add a BMS (Battery Management System) to help prevent damage to the battery, but still make sure to read all their warnings and recommended operating conditions.
Warning, don’t confuse LiFePO4 batteries with other Li ion (lithium ion) and Li-po (lithium polymer) batteries. Their maximum voltage and charging/discharging characteristics are different.
Another warning: Never short circuit a battery. The positive and negative terminals can never have a direct electrical path connecting them (including though other batteries). There has to be a current limiting load somewhere between the positive and negative terminal of each battery.
Some people abbreviate LiFePO4 even further to LFP.
Prebuilt 12.8V LiFePO4 batteries are commonly sold. 100Ah capacity is a popular size, but people often want more capacity. When multiple batteries are at the same voltage and state of charge, then all the positive terminals can be connected to all the other positive terminals, and all the negative terminals can be connected to all the other negative terminals. That way, their amp hour capacities add up.
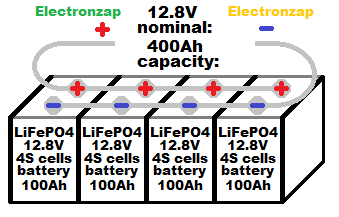
Almost all batteries are made up of cells connected in series to add up to the desired voltage, and often in parallel to increase capacity. The voltages involved with LifePO4 batteries are very similar to those of 12V, 24V etc. lead acid batteries. Therefore with some precautions, LiFePO4 can usually replace lead acid batteries in systems made for lead acid without having to make a lot of modifications.
- 3.2V to 3.65V is the typical voltage range of a LiFePO4 cell.
- 4 series cell will have a typical nominal voltage of 12.8V and charged with up to 14.6V. 4 series cells is how most batteries come unless you want to build your own battery from individual cells or buy a different voltage battery.
- When the charging voltage is removed, the charged voltage will quickly settle to about 3.4V per cell or 13.6V for 4 series cells.
- Higher voltage than 3.65V per cell/14.6V per 4 series cells battery, may damage the cell or battery.
- Lower voltage than 2.5V per cell/10V per 4 series cells, may damage the battery. To stay safe, it’s typically best to stop discharging LiFePO4 (and even li ion and LiPO) when any cells reach 3V.
- LiFePO4 is not to be charged when they are too cold. Generally below freezing (oC, 32F).
- Absorption (time): Temporarily raising the voltage of the cell’s higher than the max voltage that they provide power at once they are fully charged. That’s how you get the most charge into the battery and balance the cells.
- Float: LiFePO4 doesn’t need float. But. many chargers that also charge lead acid batteries will have a float setting. It is a voltage that the charger will hold the battery to after the battery was considered fully charged. LiFePO4 batteries hold their fully charged voltage for a long time. You can set the float voltage to that voltage.
- Note: Lead acid does not hold it’s voltage and charge over time, so a charger will keep it toped off using float. That is the main intention of float.
Upcoming topics:
Charging cycle:
- Bulk: Constant current phase.
- Absorption: Constant voltage.
- Topping charge: A charger might recharge an already charged battery whose charge went down over a period of time after it was charged. LiFePO4 hold their charge for a long time, so, this is not common.
- Float: Optional
- Equalization: Optional. (finish charging a battery that didn’t go through the full Bulk, absorption and Float charging cycle.
- C rate. 1C charging or discharging, means that the battery is getting or giving the amount of current that it is rated for in Amp hours. Commonly recommended to charge LiFePO4 batteries at 0.2C. So, a 10Ah LiFePO4 battery would be charging at 1C if it was being given 10A of current, which is really high. So, it’d be better to charge a 10Ah LiFePO4 battery at 2A (0.2C). 0.2C for a 4Ah battery would be 7Ah x 0.2C = 1.4A.
- Sleeping LiFoPO4 battery. BMS totally disconnects from the battery because it is too discharged. BMS must be woken up and battery must be recharged.
Other topics:
- BMS is circuitry often added to the battery to monitor battery parameters and take certain actions to protect it. It’s generally built into prebuilt batteries by the battery manufacturer, but of course, make sure to verify that it is.
- BMS from different brands/models might not get along together. Many manufacturers recommend combining series/parallel batteries with the same battery.
Good topics to check out next:
To support this site, check out the following links:
- Check out my YouTube videos! https://www.youtube.com/c/Electronzap/videos
- Products I used in my videos or otherwise think look like a good buy. As an Amazon associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. https://www.amazon.com/shop/electronzapdotcom
- Information on this site is not guaranteed to be accurate. Always consult the manufacturer info/datasheet of parts you use. Research the proper safety precautions for everything you do.
- Electronzap is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com.