Table of Contents
Indicator LEDs mostly provide enough light so that you can tell whether they are lit or not.
- LED = Light Emitting Diode.
- Typically have a recommended maximum current of 20mA. Limit current to less than that.
Even though LEDs provide light, they have the same basic electrical properties of other diodes.
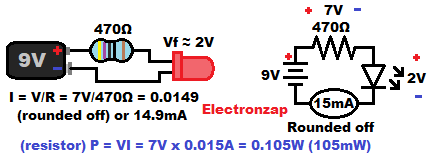
- Forward Biased: LEDs will only conduct current if their Anode if more positive than their Cathode by an amount set by their forward voltage. Typically 2V for Red LEDs, and 3V for Blue or Green LEDs.
- Protective (Current Limiting) Resistor: LEDs drop their forward voltage from the circuit, and then the rest of the supply voltage goes across a resistor when the LED is protected by a resistor. The resistor’s value will set the current.
- Current Source: A steady current, regardless of supply voltage (within limits), is a good way to power LEDs.
Multiple LEDs:
- Series LEDs stack their forward voltages/voltage drops.
- Parallel resistors should be given their own current limiting resistor/current source. One LED might pass all the current instead of all of them sharing the current equally.