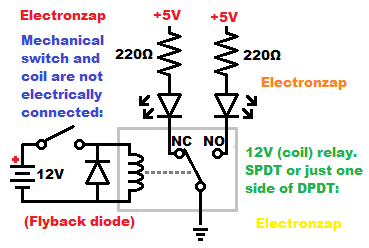
Electromagnetic Relays are mechanical switches which use magnetic fields to move the switch position. Current is run through a coil to create the magnetic field.
- Active High (module). High signals moves the switch from NC to NO and holds it there as long as the signal is applied.
- Active Low (module). Low signal moves the switch from NC to NO and holds it there as long as the low signal is applied.
- Bistable/Latching. a pulse moves the switch
The coil and switch are not electrically connected, they are electrically isolated. The coil and the load that is switched can be powered with separate power supplies. It is common to use a low voltage (for the coil) to control a high voltage (for the load being switched).
Since relays depends on an inductive coil, it is advised to use a (flyback) diode parallel to the coil. The diode is reverse biased in relationship to the power supply, which does not conduct while power is applied, and then gives a safe current path for the inductive kickback of the coil when power is cut.