Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) need to be provided a small amount of current in order to turn on a load that requires a lot more current.
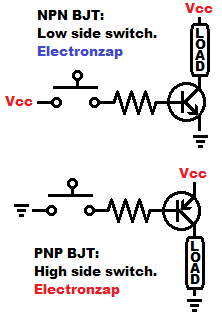
- NPN BJTs need a little Base to Emitter current in order to allow a lot more current to flow from Collector to Emitter. The BJT doesn’t set the current. The current is a signal provided by other circuitry. (Conventional current is looked at as moving from positive to negative, the opposite of electron flow).
- PNP BJTs need a little Emitter to Base current in order to allow a lot more current to flow from Emitter to Collector. (Conventional current is looked at as moving from positive to negative, the opposite of electron flow).
- The load is placed between BJT Collector and the appropriate supply voltage (+ for NPN and – for PNP).
- BJTs have an approximate gain, which is how many more times as much current will be allowed to flow between collector and emitter as is flowing through Base and Emitter.
- 100 gain NPN BJT would let up to 10mA of Collector current flow while it is provided about 0.1mA of current at the Base.
- Cut Off (Not conducting): No Base current means that there is no current allowed to pass through the collector. The load is held off completely.
- Active region (Conducting a bit): There is some Base current, but due to the gain of the BJT, not enough to get the transistor to conduct as much current as the load desires, given the supply voltage.
- Saturated (Fully conducting): There is enough Base current to allow the Collector to pass more current than the load needs. The load will set the current through it and the BJT Collector based on the supply voltage.
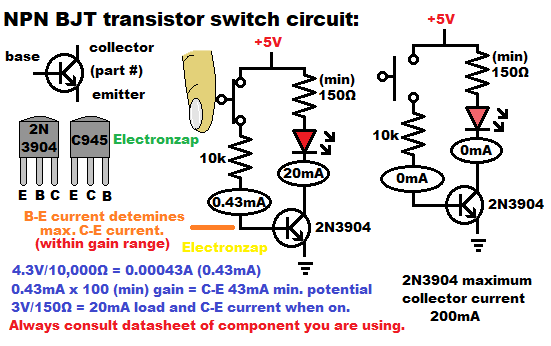
The 2N3904 is a commonly used NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor.
You’ll probably get a gain of somewhere around 100 to 300 with the 2N3904. Exact value depends on various circuit conditions outlined in the 2N3904 datasheet (google search: 2N3904 datasheet).
You’ll probably be fine just assuming that the 2N3904 has a gain of at least 100.