Table of Contents
Currently (2024) batteries are primarily used to store power in a few ways:
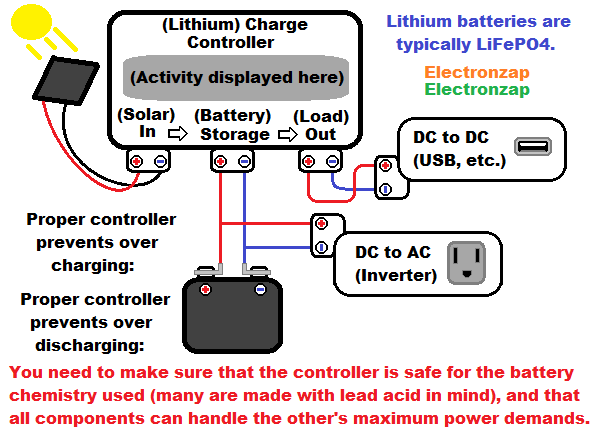
- Storing power from solar panels until it is needed:
- Storing power for when the grid goes down for a while.
- Portable devices and electric vehicles.
A battery is made up of cells, which are made up of various combinations of chemistry.
You can’t change the electrical properties of a given cell chemistry, but you can connect the cells in series and/or parallel to increase the usable voltage and/or current that it can provide.
LiFePO4
If you are designing a power bank these days (2024) you are probably going to use LiFePO4 to store power. But, only do so if it is the best option. Don’t assume it is the best option just because it usually is.
- Lighter and cheaper than Lead Acid.
- Lead acid can be charged below freezing (LiFePO4 can’t), so it is still used in fuel powered automobiles.
- Less fire prone than other li ion batteries. (not usually referred to as being a li ion battery)
- 1 cell
- 3.65V is the temporary maximum charging voltage (to pump the most charge into the cell).
- 3.4V is the resting voltage after a cell has been charged.
- 3.2V is the nominal voltage of cell. Average voltage when going from fully charged to fully discharged.
- 3V is a very discharged cell. Good time to stop using until it is at least partially recharged.
- 2.5V is a completely discharged cell. Damage may be caused if it is discharged any further, and it is highly recommended it be recharged at least partially as soon as possible.
- Less fire prone than other li ion batteries.
- 4 series cells (common battery to use for 12V circuits). Keep in mind that the actual voltage is almost always above 12 volts.
- 14.6V is the temporary maximum charging voltage (to pump the most charge into the cell).
- 13.6V is the resting voltage after a cell has been charged.
- 12.8V is the nominal voltage of cell. Average voltage when going from fully charged to fully discharged.
- 12V is a very discharged cell. Good time to stop using until it is at least partially recharged.
- 10V is a completely discharged cell. Damage may be caused if it is discharged any further, and it is highly recommended that it be recharged at least partially as soon as possible.
- Can be partially charged and/or partially used at any time. There’s no benefit to fully charging and discharging LiFePO4 with each use if you don’t need to use a full charge.
Lithium Ion (li ion):
Commonly used in portable devices in a way similar to AA or D cell alkaline batteries. The most well known package is the 18650 cell, which looks like a AA battery, but is quite a bit larger. Li ion is rechargeable, and many portable devices contain (micro) USB ports to charge the battery without having to remove it from the device.
- One cell (such as an 18650)
- Fully charged: 4.2V
- Nominal voltage: 3.6V
- Fully discharged: 3.2V
Lead Acid:
Used mostly to start combustion automobile engines, due to being able to be charged in colder weather than LiFePO4, and being able to provide high current for short periods of time.
Page not finished:
More will be added to this page later: