A voltage source maintains a voltage across a load.
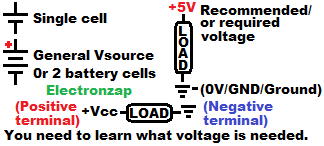
A voltage source also needs to provide current. If it can not provide enough current to power a load, then it won’t work as a voltage source for that load.
- Bench power supply: Typically used as an adjustable DC voltage source.
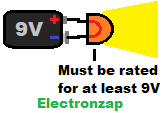
Incandescent light bulbs can be connected directly to a voltage they are rated for. - Battery: DC voltage is set by battery chemistry, number of series cells/batteries, and state of charge.
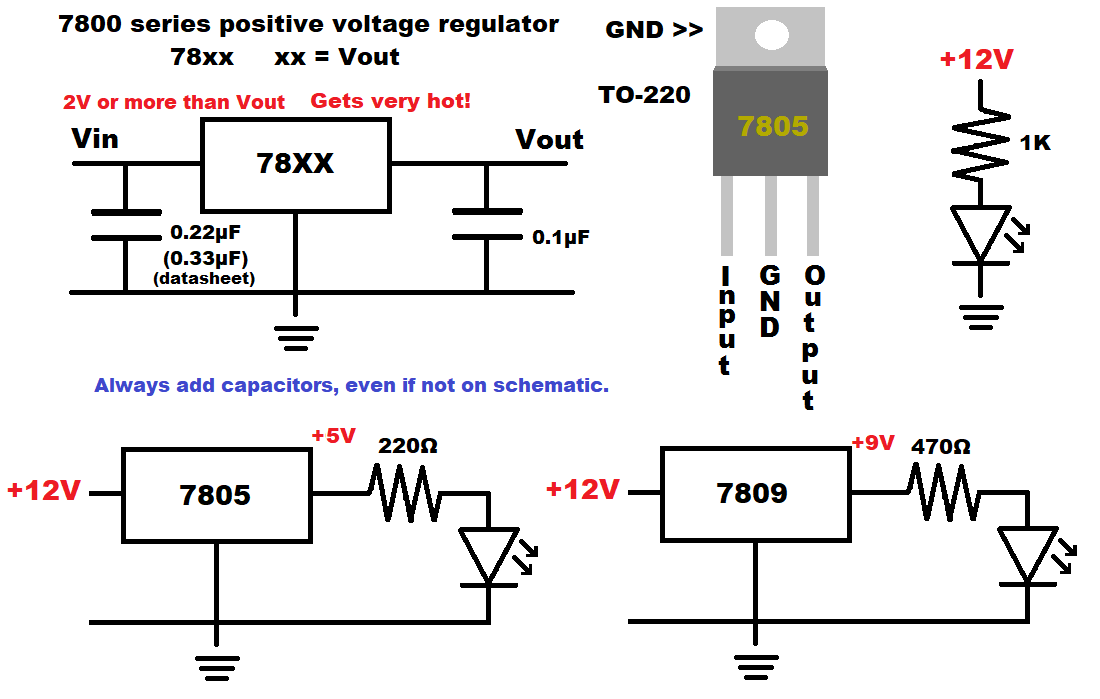
- Voltage regulator: Maintains a voltage across the load, but the actual power (voltage and current) comes from a higher voltage source. The voltage dropped is simply wasted as extra heat.
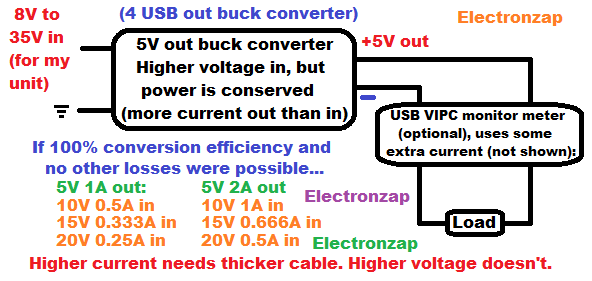
- Buck/Boost converter: Takes the power from a power source, and either converts some of the current into a higher voltage (boost) at a lower current, or it converts some of the voltage into extra current (Buck) at a lower voltage. Little power is wasted as heat. The more efficient of a conversion, the better.