Table of Contents
While lighting an LED with a 12V LiFePO4 battery, it must be taken into consideration that the battery might be charged while the LED is being lit. LiFePO4 chargers commonly charge the battery at 14.6V. So it is a good idea to design any circuit connected to the battery to be able to handle that 14.6V instead of the 13.6V that a fully charge 12V LiFePO4 battery will quickly settle to right after it has been charged.
A 1/4W 1,000Ω resistor that is protecting an LED from 14.6V will get hotter than desired. The LED will drop about 2V (red) or 3V (blue) of the voltage that makes it to the resistor. Therefore the resistor can be expected to have about 12.6V across it, out of the 14.6V total. Keep in mind that it is recommended to keep a resistor below 1/8W (0.125W) when it is rated for a maximum of 1/4W (0.25W).
- 12.6V/1,000Ω = 0.0126A (12.6mA)
- 0.0126A x 12.6V = 0.15876W
If you put two 500Ω resistor in series, then they will provide a total of 1,000Ω of resistance. The same amount of current will flow through the circuit. Each of the 2 series resistors however, will only do half of the current limitation work. That’s because 0.0126A of current flowing through a 500Ω resistor means that there is 0.0126A x 500Ω = 6.3V across each resistor. They both get half as hot as a lone 1,000Ω resistor would get in their place.
- 0.0126A x 6.3V = 0.07938W of power that each of the 2 series 500Ω resistors needs to dissipate.
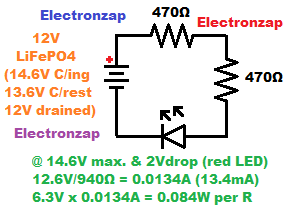
470Ω is just a little bit less resistance than 500Ω but is a much more commonly available value of a resistor. Using 2 series 470Ω resistors instead of 2 series 500Ω resistors will result in a little more current flow, and a little more heat generated by each resistor.
Pages to more example circuits:
Making some pages now. Links will be added.
To support this site, check out the following links:
- Check out my YouTube videos! https://www.youtube.com/c/Electronzap/videos
- Products I used in my videos or otherwise think look like a good buy. As an Amazon associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. My Amazon affiliate page showing products I think look good
- Information on this site is not guaranteed to be accurate. Always consult the manufacturer info/datasheet of parts you use. Research the proper safety precautions for everything you do.
- Electronzap is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com.