Table of Contents
Most people start off learning electronics by studying the effects of resistance on electricity. It helps to understand those principles, by measuring them with a multimeter.
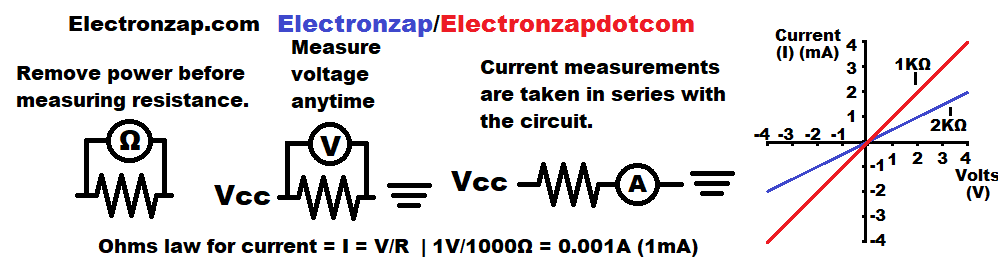
- Resistance can be measure directly as long as no power is being applied to the resistance. Just set the meter to measure resistance, and place the probes on both sides of the resistance.
- Voltage across a resistance can always be measured. In fact, that’s one of the most useful measurements that you can take. Simply set the multimeter so that it can measure more voltage than you will be measuring, and touch the probes on both sides of the resistance while it is being powered.
- Voltage (V) pushes current (I) through a resistance (R). 1 volt pushes 1 amp of current through 1 ohm of resistance. That produces 1 watt of power, which is a lot more power than most basic electronic components can handle. In most electronic circuits, resistance is usually a lot higher, while voltage is a bit higher, and current is a lot lower. Ohms law for current is …. I = V/R. Current (in amps) equals voltage (in volts) divided by resistance (in ohms).
- Current is the trickiest measurement to make.
- You need a complete circuit which is also opened up. You will need to break the connection of part of the conductive path of the circuit, in order to measure the current through the circuit.
-
- However! An open switch has already opened up the circuit. You can simply connect the meter to both sides of the switch. The meter will turn the circuit on instead of the switch, and measure the current flow.
-
- The multimeter has to be set to measure a current higher than what you will measure.
- If you measure a current that is higher than what the meter is set to measure, then you will probably blow a fuse and might damage the meter.
- The gap (open) in the circuit needs to be bridged with the meter. The meter is actually measuring how much current flows through it. Series components pass the same amount of current.
- You need a complete circuit which is also opened up. You will need to break the connection of part of the conductive path of the circuit, in order to measure the current through the circuit.
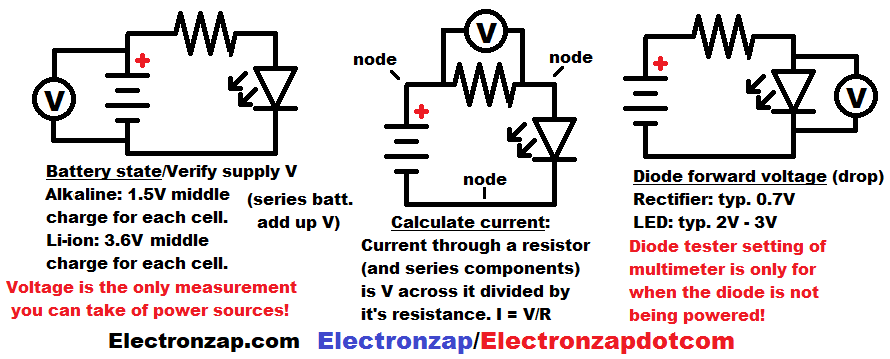
You can measure the voltage across any component, including the power source. The power supply/battery voltage will be split up across series components based on each one of their electrical properties. Therefore, it is important to know how much of that voltage each component has across it.
Videos:
Measuring resistance:
Measuring voltage:
Measuring current:
To support this site, check out the following links:
- Become a Patron!
- Check out my YouTube videos! https://www.youtube.com/c/Electronzap/videos
- Products I used in my videos or otherwise think look like a good buy. As an Amazon associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. https://www.amazon.com/shop/electronzapdotcom
- Information on this site is not guaranteed to be accurate. Always consult the manufacturer info/datasheet of parts you use. Research the proper safety precautions for everything you do.
- Electronzap is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com.