Table of Contents
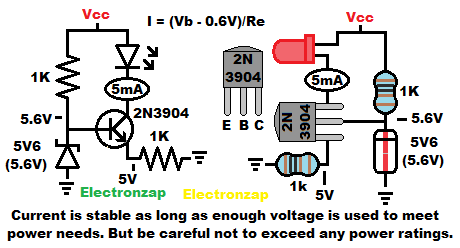
NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) collector current also has to flow through the emitter.
- Emitter resistor has the base voltage minus approx. 0.6V across it. 5.6V – 0.6V = 5V in the diagram.
- Based on that voltage, and the resistor resistance, the amount of current that flows through them is calculated with ohms law. 5V/1,000Ω = 0.005A (5mA) in the diagram example.
- Collector to emitter passes virtually all of the current that flows through the emitter resistor in order to maintain that voltage.
- A load between the supply voltage and collector is in series with collector and emitter. Therefore it passes that same amount of current, as long as there is enough supply voltage available to do so.
- The NPN BJT transistor actually sinks current. That is because the load is on the high side of the transistor. However, anything that sets a certain amount of current is commonly referred to as a current source.
- A 5.6V reverse biased zener diode is used in my example to set the emitter voltage to approx. 5V. That’s true even as the supply voltage changes by a lot. Lots of zener diodes are 0.6V higher than a commonly desired voltage because of the NPN BJT Base to Emitter diode drop.
Video:
To support this site, check out the following links:
- Become a Patron!
- Check out my YouTube videos! https://www.youtube.com/c/Electronzap/videos
- Products I used in my videos or otherwise think look like a good buy. As an Amazon associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. https://www.amazon.com/shop/electronzapdotcom
- Information on this site is not guaranteed to be accurate. Always consult the manufacturer info/datasheet of parts you use. Research the proper safety precautions for everything you do.
- Electronzap is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com.